ASID Algorithms
ASID library is designed to deal with data scarcity problems in tabular ML tasks. These mainly include an insufficient number of available samples or lack of instances of a certain class.
Small dataset problem
Small datasets prevail in real life, whereas statistical inference from limited data remains a challenging task. Insufficient sample size leads to poor performance of machine learning algorithms. ASID library exploits a synthetic dataset generation approach to deal with small dataset problem. Limited tabular data is usually modelled with more straightforward methods, which involve explicit density estimation. These methods include kernel density estimation, gaussian mixture models and copulas.
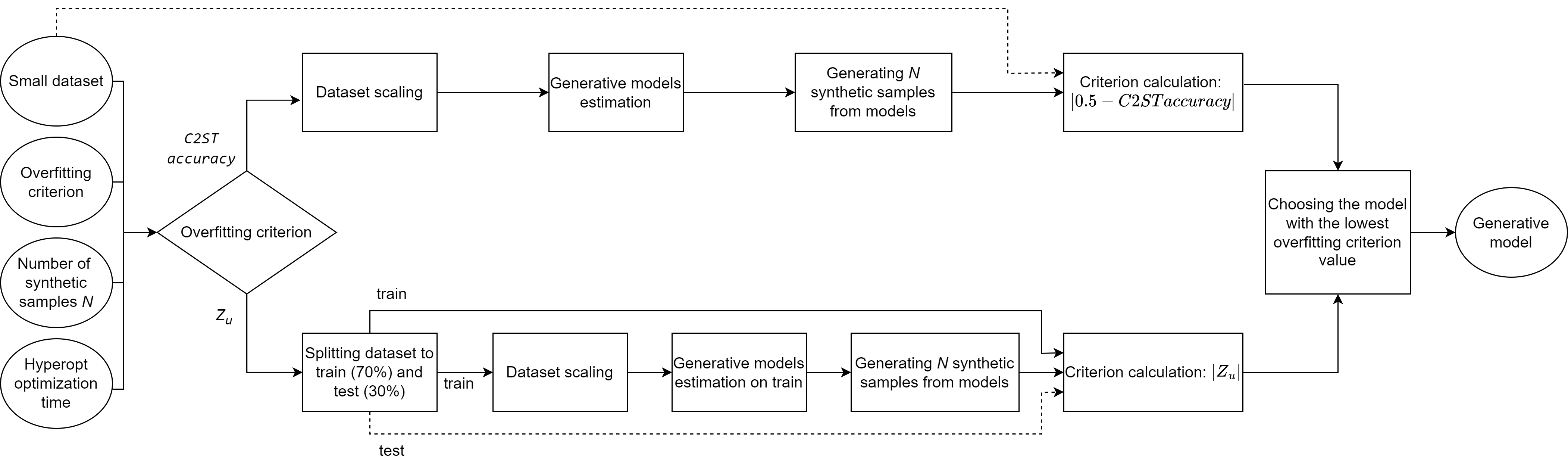
While fitting a generative model one of the main challenges is to find balance between the similarity of synthetic sample and generalization ability of the resulting model. For this reason, model overfitting should be thoroughly examined. One of the indicators that are able to detect this is Classifier Two-Sample Test (C2ST). It is based on a 1-Nearest Neighbor binary classifier, which is trained to discriminate between the initial and generated samples. After that it computes the leave-one-out (LOO) accuracy separately for the real and generated samples [1]. In addition to that, a Data-Copying Test was proposed in [2]. It calculates distances from training set to the test and generated ones using 1-Nearest Neighbor algorithm. After that it applies Mann-Whitney U Test to the obtained distance sets. The resulting statistic Zu gets negative value, if model is overfitted and generated sample is closer to train one than to test sample.
Synthetic dataset generation in ASID
GenerativeModel estimator searches through a number of generative algorithms for tabular data and returns an optimal option in terms of overfitting. The list of generative models includes:
Kernel density estimation (scikit-learn and statsmodels implementations);
Gaussian mixture models (scikit-learn implementations);
Copula (SDV Tabular implementation);
GAN and VAE-based models for tabular data (SDV Tabular implementations).
Generative models are fitted with Hyperopt optimization where applicable. Further, overfitting for each option is estimated based on synthetic samples and one of the indicators: c2st_acc (Classifier Two-Sample Test) or zu (Zu statistic). As a result, GenerativeModel estimator outputs an optimal model, which has the best overfitting criterion value.
Imbalance problem
The dataset is considered imbalanced if one class significantly dominates another by the sample size. However, the imbalance ratio, which deteriorates the classification performance, depends on the dataset characteristics. In general, the existing studies focus on the imbalance ratios ranging from 1:4 to 1:100 [3]. Standard machine learning frameworks without special preprocessing methods show poor performance on imbalanced datasets as they assume equal misclassification costs for every class. Therefore, they tend to favor the majority class and may output a lower accuracy for the minority one.
One of the most common approaches for imbalanced learning on tabular data is a combination of data-level balancing procedures and ensemble algorithms. Data-level algorithms modify the train sample by adding synthetic instances or removing the original ones, to make a dataset suitable for the standard machine learning frameworks. In general, data-level procedures are applied as a preprocessing step or built into the hybrid classifiers tailored for imbalanced learning.
AutoBalanceBoost
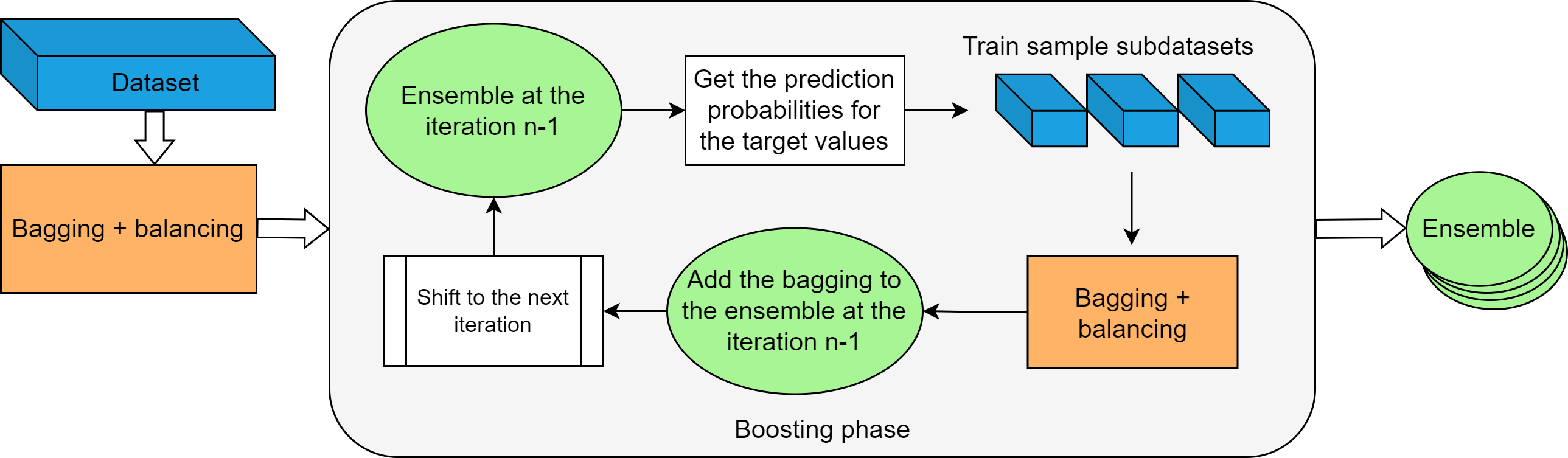
AutoBalanceBoost estimator is a tailored classifier for imbalanced learning tasks. It combines a consistent ensemble classifier with an oversampling technique. It takes an advantage of the two popular ensemble approaches: bagging and boosting. Another benefit consists in the embedded sequential parameter tuning scheme, which allows to get the high accuracy without a time-consuming exhaustive search. Empirical analysis showed, that ABB demonstrated a robust performance on a variety of imbalanced datasets and on average outperforms the competitors.
Imbalanced learning in ASID
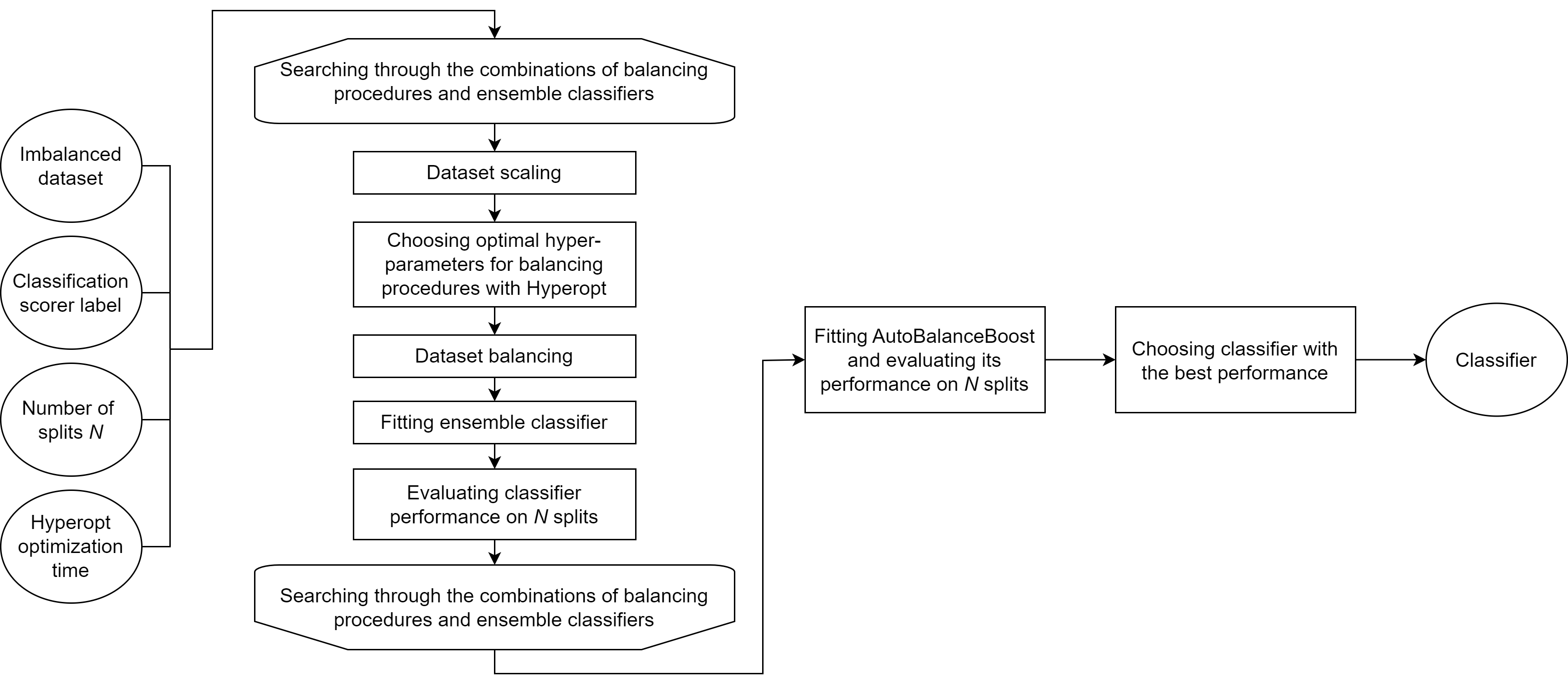
ImbalancedLearningClassifier estimator looks through the every combination of balancing procedures and ensemble classifiers. The list of balancing algorithms includes oversampling and undersampling procedures taken from imbalanced-learn library: RandomOverSampler, RandomUnderSampler, SMOTE, ADASYN. Ensemble classifiers comprise such state-of-the-art algorithms as XGBoost, Random Forest, LightGBM and Catboost. In addition to that, AutoBalanceBoost result is also included into the comparison. As a result, ImbalancedLearningClassifier estimator outputs classifier with the best performance.
References
Xu, Q., Huang, G., Yuan, Y., Guo, C., Sun, Y., Wu, F., & Weinberger, K. (2018) “An empirical study on evaluation metrics of generative adversarial networks” arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.07755.
Meehan C., Chaudhuri K., Dasgupta S. (2020) “A non-parametric test to detect data-copying in generative models” International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics.
Krawczyk, Bartosz. ”Learning from imbalanced data: open challenges and future directions.” Progress in Artificial Intelligence 5.4 (2016): 221-232.